Opening the Benefits of Diatomaceous Planet Filtering System for Clean and pure Water
The expedition of diatomaceous planet (DE) filtering system offers an engaging choice for those seeking sustainable and efficient water filtration approaches. As the need for tidy water continues to climb globally, comprehending the complex applications and advantages of DE filters may reveal crucial insights for both home and commercial usage.
What Is Diatomaceous Planet?
Diatomaceous planet, often referred to as DE, is a normally happening sedimentary rock composed mainly of the fossilized remains of little, water organisms referred to as diatoms. These single-celled algae are abundant in silica, which is the primary element of DE. The distinct structure of diatomaceous planet is composed of tiny, porous fragments that supply a high area, making it an effective filtering medium.
DE is generally harvested from old lake beds and deposits, which have actually accumulated over hundreds of years. It shows up as a fine, white to beige powder, and its chemical composition mostly includes silicon dioxide, along with trace quantities of various minerals. This structure is what offers DE its amazing residential properties.
Along with its application in water purification, diatomaceous earth is used in a variety of sectors, including farming, food storage, and bug control. Its ability to soak up moisture and its unpleasant high qualities make it a useful resource in these fields. Overall, diatomaceous earth stands apart as an environmentally pleasant option for different applications due to its all-natural origin and performance in filtration procedures.

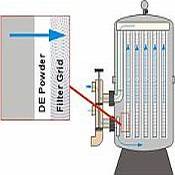
How Diatomaceous Planet Filtering Works

When water goes through a diatomaceous planet filter, the fine particles are caught in the complex network of small pores. The shapes and size of these pores are essential, as they are developed to target particular pollutants while allowing clean water to move through. As water steps with the filter medium, the mechanical activity of the diatomaceous planet catches bigger particles, while smaller sized impurities are taken in or physically obstructed.
Moreover, the area given by diatomaceous planet is comprehensive, enhancing its capacity to hold pollutants. This results in a steady buildup of caught particles, which can be periodically eliminated through a backwashing procedure. This technique guarantees regular filtration efficiency and adds to the total efficiency of keeping pure and tidy water.
Advantages Over Typical Filtering
When comparing diatomaceous earth filtering to conventional purification techniques, several benefits emerge that enhance water filtration performance. Among the primary advantages is the exceptional purification capability of diatomaceous earth (DE), which can get rid of smaller bits and navigate to this site impurities that traditional filters might miss out on. The microscopic framework of DE allows it to catch impurities, consisting of germs and protozoa, causing cleaner water.
Furthermore, diatomaceous planet filters tend to have a longer lifespan than conventional media, lowering the frequency of replacement and upkeep. This longevity not just decreases operational costs yet also lessens waste, adding to even more lasting practices. DE filters likewise run at reduced stress, which can bring about energy cost savings in massive applications.
An additional significant advantage is the flexibility of diatomaceous planet. It can be made use of efficiently in different contexts, from local water therapy centers to specialized commercial applications (diatomaceous earth filtering). The all-natural composition of DE makes it an environment-friendly choice, devoid of dangerous chemicals and toxins frequently related to synthetic filtering systems
Applications in Home and Sector
Numerous applications of diatomaceous earth filtering can be found in both household and commercial settings, highlighting its versatility and efficiency in water filtration. In property settings, diatomaceous earth (DE) filters are generally used in pool, properly recording particles and microorganisms, consequently preserving water clearness and health. Furthermore, numerous families utilize DE in home water filtration systems, where it offers to get rid of pollutants, sediment, and damaging pathogens, ensuring safe alcohol consumption water.
In industrial applications, diatomaceous planet filtering is integral to numerous markets, including food and beverage production, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater therapy. In the food market, DE is used in the purification of beer and red wine, facilitating the elimination of yeast and other particulates while preserving the drink's flavor profile. In wastewater therapy facilities, DE filters play a crucial function in enhancing water high quality by capturing pollutants and promoting the recycling of water resources.
The performance of diatomaceous earth in both family and commercial applications highlights its invaluable function in advertising clean water accessibility, contributing to public health and wellness, and sustaining sustainable methods.
Choosing the Right DE Filter
Choosing the ideal diatomaceous planet (DE) filter is important for making sure optimum water filtration, whether for residential or industrial usage. diatomaceous earth filtering. The selection of a DE filter relies on several vital aspects, consisting of the details application, circulation price needs, and the preferred level of filtration
First, evaluate the volume of water to be filtered. For household usage, smaller filters are adequate, while industrial applications may require larger, high-capacity systems. Next off, consider the circulation price; it is necessary to pick a filter that can take care of the called for throughput without endangering water top quality.
Furthermore, examine the filtering degree; DE filters been available in different grades, affecting the elimination of contaminations and particulates. Higher-grade filters are excellent for applications requiring strict purity degrees.
Last but not least, take into consideration the maintenance requirements and the schedule of read review substitute DE powder. Filters that are simpler to maintain and have conveniently available materials will lower downtime and operational costs. By meticulously taking you could try here into consideration these elements, one can pick a DE filter that meets certain requirements, ensuring the distribution of tidy and secure water.
Conclusion
In summary, diatomaceous earth filtering system stands for a considerable improvement in water filtration technology, offering enhanced effectiveness and efficiency in recording contaminations. Accepting diatomaceous planet filtering system can lead to boosted public health outcomes and greater access to tidy water.
The exploration of diatomaceous earth (DE) filtering provides a compelling option for those seeking lasting and reliable water filtration approaches.When contrasting diatomaceous planet filtering system to standard filtration methods, a number of advantages emerge that enhance water purification efficiency.Countless applications of diatomaceous earth filtering can be located in both household and commercial setups, highlighting its convenience and performance in water purification. In household settings, diatomaceous planet (DE) filters are frequently utilized in swimming pools, successfully catching debris and microorganisms, consequently keeping water quality and health. In wastewater therapy facilities, DE filters play a vital function in improving water quality by trapping contaminants and facilitating the recycling of water sources.